How To SSH Into Raspberry Pi From Another Network: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you looking for a way to remotely access your Raspberry Pi from another network? If so, you're in the right place. Secure Shell (SSH) is a powerful protocol that allows you to control your Raspberry Pi from anywhere in the world. Whether you're managing a home server, running a project, or troubleshooting remotely, SSH is an essential tool for Raspberry Pi users. In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about setting up SSH access to your Raspberry Pi from another network, ensuring a secure and reliable connection.
SSH access is particularly useful when you need to manage your Raspberry Pi without being physically present. However, accessing your Raspberry Pi from another network requires additional steps to ensure your connection is secure and functional. This guide will cover the basics of SSH, how to enable it on your Raspberry Pi, and the steps to configure your network for remote access. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to SSH into your Raspberry Pi from anywhere in the world.
Before we dive into the details, it’s important to note that SSH is a powerful tool, and improper configuration can expose your device to security risks. Therefore, we’ll also discuss best practices for securing your SSH connection. This article is designed to be beginner-friendly while also providing advanced tips for experienced users. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- What is SSH and Why is it Important?
- How to Enable SSH on Your Raspberry Pi
- Configuring Your Network for Remote Access
- Setting Up Port Forwarding on Your Router
- Using Dynamic DNS for Remote Access
- Choosing the Right SSH Client
- Securing Your SSH Connection
- Troubleshooting Common SSH Issues
- Advanced Tips for SSH Users
- Conclusion: Mastering Remote Access with SSH
What is SSH and Why is it Important?
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol used for secure communication between two devices over an unsecured network. It provides a secure channel for executing commands, transferring files, and managing remote systems. SSH is widely used by developers, system administrators, and hobbyists to manage servers, IoT devices, and other networked systems.
One of the key advantages of SSH is its encryption capabilities. Unlike other protocols, SSH encrypts all data transmitted between the client and the server, ensuring that sensitive information, such as login credentials, cannot be intercepted by malicious actors. This makes SSH an essential tool for anyone managing a Raspberry Pi remotely.
For Raspberry Pi users, SSH is particularly valuable because it allows you to access your device without needing a monitor, keyboard, or mouse. Whether you’re running a home automation system, hosting a web server, or experimenting with IoT projects, SSH enables you to control your Raspberry Pi from anywhere in the world.
How to Enable SSH on Your Raspberry Pi
Before you can SSH into your Raspberry Pi, you need to enable the SSH service. By default, SSH is disabled on Raspberry Pi OS for security reasons. Here’s how you can enable it:
Using the Raspberry Pi Configuration Tool
- Open the terminal on your Raspberry Pi or connect a monitor and keyboard.
- Type
sudo raspi-configand press Enter. - Navigate to "Interfacing Options" and select "SSH."
- Choose "Yes" to enable SSH and exit the configuration tool.
Using the Desktop Interface
- Click on the Raspberry Pi menu and go to "Preferences"> "Raspberry Pi Configuration."
- In the "Interfaces" tab, enable SSH by selecting "Enabled."
- Click "OK" to save your changes.
Creating an Empty File on the Boot Partition
- If you don’t have access to the desktop or terminal, you can enable SSH by creating an empty file named
ssh(without any extension) in the boot partition of your Raspberry Pi’s SD card. - Insert the SD card into your computer, create the file, and eject it safely.
- When you boot your Raspberry Pi, it will automatically enable SSH.
Configuring Your Network for Remote Access
Once SSH is enabled, the next step is to configure your network to allow remote access. This involves setting up your Raspberry Pi’s IP address and ensuring it remains consistent.
Assigning a Static IP Address
By default, your Raspberry Pi may use a dynamic IP address assigned by your router’s DHCP server. However, dynamic IP addresses can change over time, making it difficult to connect remotely. To avoid this, assign a static IP address to your Raspberry Pi:
- Log in to your router’s admin panel and navigate to the DHCP settings.
- Find your Raspberry Pi in the list of connected devices and assign it a static IP address.
- Alternatively, configure a static IP address directly on your Raspberry Pi by editing the
dhcpcd.conffile:
Edit the file using the command:
sudo nano /etc/dhcpcd.confAdd the following lines, replacing the values with your network settings:
interface eth0
static ip_address=192.168.1.100/24
static routers=192.168.1.1
static domain_name_servers=8.8.8.8 Testing Your Connection
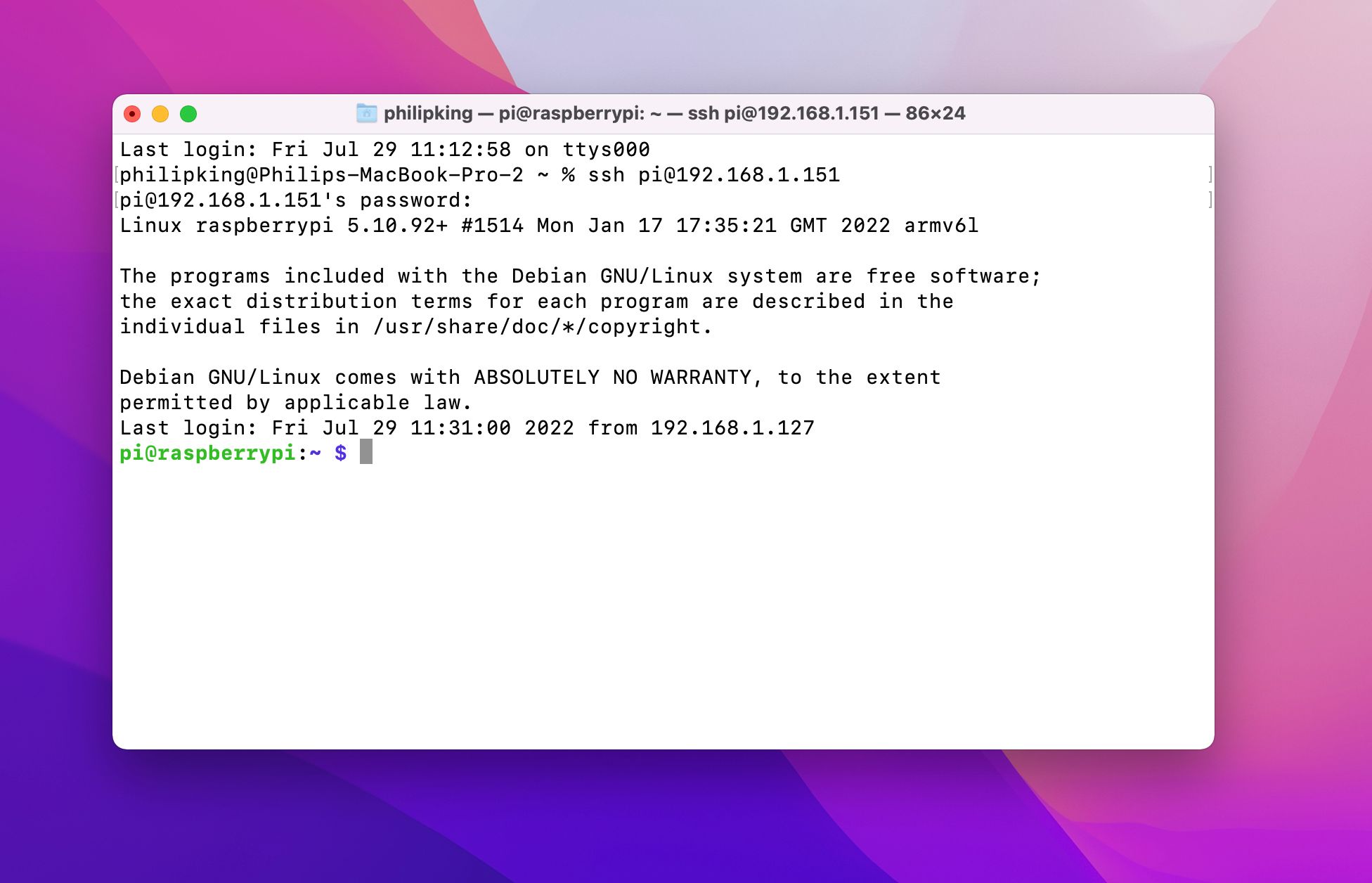
After assigning a static IP address, test your SSH connection from another device on the same network:
- Open a terminal or SSH client and type:
ssh pi@192.168.1.100Replace 192.168.1.100 with your Raspberry Pi’s IP address. If the connection is successful, you’re ready to proceed to the next step.
Setting Up Port Forwarding on Your Router
To access your Raspberry Pi from another network, you need to configure port forwarding on your router. Port forwarding allows external devices to connect to your Raspberry Pi by forwarding incoming traffic on a specific port to your device’s IP address.
Steps to Configure Port Forwarding
- Log in to your router’s admin panel using its IP address (e.g.,
192.168.1.1). - Navigate to the "Port Forwarding" or "NAT" section.
- Create a new rule with the following details:
- Service Name: SSH
- External Port: 22
- Internal IP Address: Your Raspberry Pi’s static IP address
- Internal Port: 22
- Protocol: TCP
Save the rule and exit the admin panel. Your router will now forward incoming SSH traffic to your Raspberry Pi.
Testing External Access
To test your setup, use your public IP address to connect to your Raspberry Pi from an external network:
ssh pi@your-public-ipReplace your-public-ip with your router’s public IP address, which you can find by searching "What is my IP" on Google.
Using Dynamic DNS for Remote Access
If your internet service provider assigns you a dynamic public IP address, it may change periodically, making it difficult to connect to your Raspberry Pi. To solve this issue, you can use a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service.
Setting Up Dynamic DNS
- Sign up for a DDNS service such as No-IP, DuckDNS, or Dynu.
- Create a hostname (e.g.,
myraspberrypi.ddns.net) and link it to your public IP address. - Install a DDNS client on your Raspberry Pi to update the hostname whenever your public IP changes:
sudo apt install ddclientFollow the prompts to configure the client with your DDNS provider’s details.
Connecting via DDNS
Once DDNS is set up, you can connect to your Raspberry Pi using the hostname:
ssh pi@myraspberrypi.ddns.netChoosing the Right SSH Client
There are several SSH clients available for different operating systems. Here are some popular options:
- Windows: PuTTY is a lightweight and user-friendly SSH client.
- macOS and Linux: The built-in terminal supports SSH commands.
- Mobile Devices: Apps like Termius and JuiceSSH provide SSH access on the go.
Securing Your SSH Connection
Security is paramount when enabling remote access to your Raspberry Pi. Here are some best practices to secure your SSH connection:
Change the Default Password
The default username and password for Raspberry Pi are well-known, making it vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Change the password immediately:
passwdDisable Password Authentication
Use SSH keys for authentication instead of passwords. Generate an SSH key pair on your client machine:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096Copy the public key to your Raspberry Pi:
ssh-copy-id pi@192.168.1.100Disable password authentication by editing the SSH configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configSet the following options:
PasswordAuthentication no
PermitRootLogin no Troubleshooting Common SSH Issues
If you encounter issues while setting up SSH, here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Connection Refused: Ensure SSH is enabled and the port is open.
- Timeout Error: Check your firewall and router settings.
- Permission Denied: Verify your username, password, or SSH key.
Advanced Tips for SSH Users
For advanced users, here are some additional tips to enhance your SSH experience:
- Use
tmuxorscreento keep sessions alive. - Set up SSH tunnels for secure data transfer.
- Automate tasks using SSH scripts.
Conclusion: Mastering Remote Access with SSH
In this guide, we’ve covered everything you need to know about SSH into your Raspberry Pi from another network. From enabling SSH and configuring your network to securing your connection and troubleshooting issues, you now have the tools to manage your Raspberry Pi remotely with confidence.
Remember to prioritize security by using strong passwords, enabling SSH keys, and keeping your system updated. With these best practices in place, you can enjoy the convenience and flexibility of remote access without compromising your device’s safety.
We hope this guide has been helpful! If you have any questions or tips to share, feel free to leave a comment below. Don’t forget to share this article with others who might find it useful and explore more guides on our site to enhance your Raspberry Pi skills.
Article Recommendations

Detail Author:
- Name : Elyssa Rolfson
- Username : destini.willms
- Email : hank28@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 2000-11-17
- Address : 92888 Summer Fords Apt. 324 Wiegandfort, MO 52232
- Phone : +1-571-476-3972
- Company : Oberbrunner, Howe and Towne
- Job : Central Office Operator
- Bio : Quasi iste laboriosam illo nisi laborum qui. Harum rerum ducimus corrupti sint. Voluptas sapiente alias est rerum fuga sed consequuntur.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/jadyn_schaefer
- username : jadyn_schaefer
- bio : Et iusto est perspiciatis deleniti mollitia.
- followers : 4221
- following : 445
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/jadynschaefer
- username : jadynschaefer
- bio : Et nihil facere sed cumque eum.
- followers : 2866
- following : 757